# 装饰器
decorator 装饰器是用来注释或修改类和类方法的一种语法。
@testable // 标记当前类是测试类
class Foo {
@enumerable(true) // 当前方法可枚举
method() {}
}
1
2
3
4
5
2
3
4
5
# 类的装饰
通过装饰器可以给类添加一些属性:
function testable(target) {
target.isTest = true;
}
@testable
class Foo {
// ...
}
Foo.isTest; // true
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
如上代码, @testable 装饰器给类 Foo 添加了一个静态属性 isTest,
装饰器的第一个参数 target 就是类 Foo 它本身。
上面的代码可以看作如下:
@testable
class Foo {}
// 等同于
calss Foo {}
Foo = testable(Foo) || Foo;
1
2
3
4
5
6
2
3
4
5
6
装饰器其实就是一个对类进行处理的函数而已,第一个参数就是这个被装饰的目标类;
# 给装饰器传参
function testable(isTest) {
// 装饰器内返回一个函数
return function (target) {
target.isTest = isTest;
};
}
@testable(true)
class Foo {}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
通过给装饰器传参,我们可以用来扩展类的方法,比如:
function mixins(...funs) {
return function (target) {
Object.assign(target.prototype, ...funs);
};
}
class Foo {
say() {
console.log("hello");
}
}
@mixins(Foo)
class MyClass {}
let mycls = new MyClass();
mycls.say(); // hello
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
# 方法的装饰
装饰器不仅可以装饰类,还能够装饰类的属性
function reayonly(target, name, descriptor) {
// 修改被装饰的属性为只读
descriptor.writable = false;
return descriptor;
}
class Person {
@reayonly
hello() {
return "你好";
}
}
let p = new Person();
p.name = "haha"; // Error
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
此时 Person 类的 hello 属性不能被赋值, 装饰器 reayonly 接收三个参数:
- target: 类的原型对象,此处是
Person.prototype - name: 属性名,此处是
name - descriptor: 当前属性的描述
reayonly(Person.prototype, "name", descriptor);
// 等同于
Object.defineProperty(Person.prototype, "name", descriptor);
1
2
3
2
3
# 装饰器原理
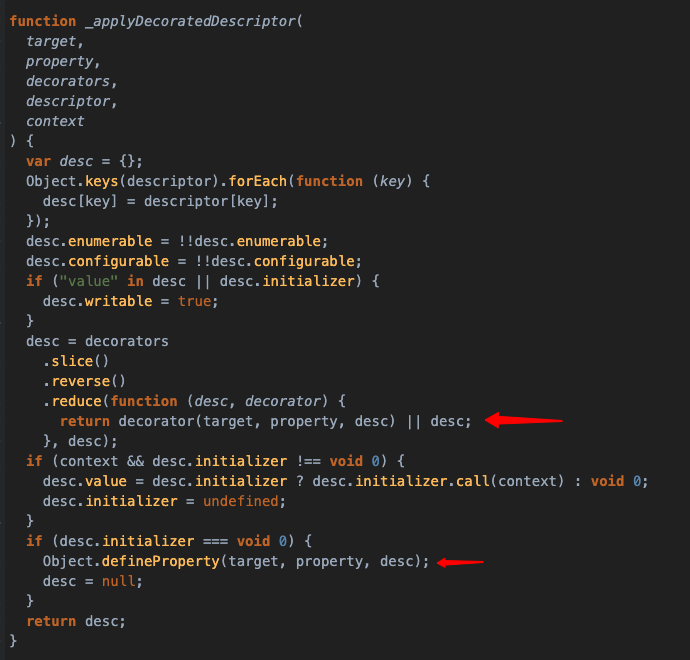
装饰器的原理其实就是利用 Object.defineProperty() 方法来实现的:
const desc = decorator(target, property, descriptor) || descriptor;
Object.defineProperty(target, property, desc);
1
2
2
装饰器返回新的描述对象,然后重新赋值
附上编译后的 ES5 代码:
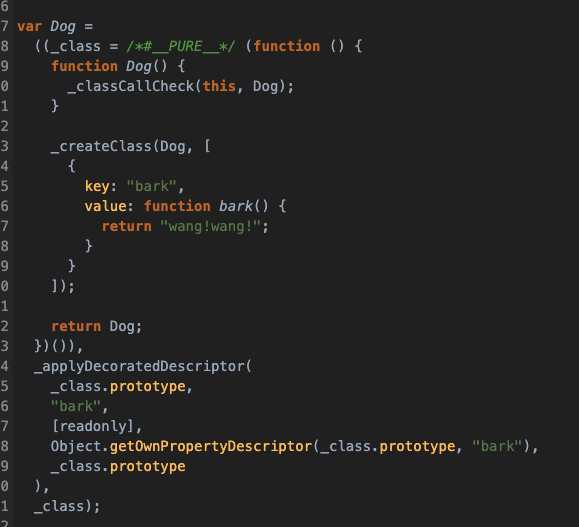
# 装饰器不能用于函数
装饰器之能用于类和类的方法,不能用于函数,因为存在函数提升
var counter = 0;
var add = function () {
counter++;
}
@add
function Foo {}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
忽略报错提示,按愿意,counter 应该等于 1 ,但其实 counter 还是 0,因为上面代码转换一下如下:
var counter;
var add ;
@add
function Foo () {}
counter = 0;
add = function () {
counter++
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12